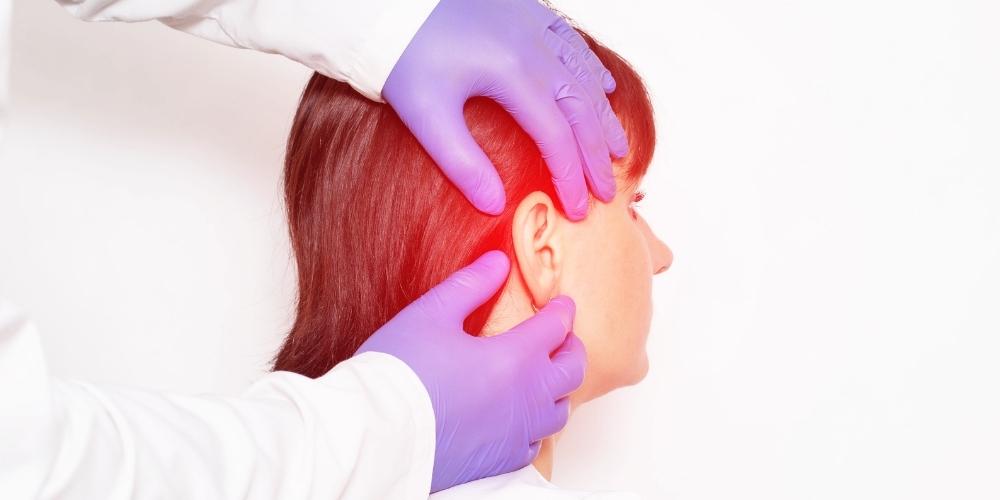
External ear infections are one of the most common ear infections and usually occur in the summer months when activities such as the sea and pool are intense. Environments with hot weather and high humidity are among the important risk factors for external ear infections.
Infections caused by bacteria, viruses, and fungi are also common in the community. Infections that are easy to treat in the early stages can affect other parts of the body later on, so timely treatment is important.
What is an external ear infection?
External ear infections are called "otitis externa" and describe inflammation of the external ear canal, which lies between the eardrum and the pinna. Commonly referred to as "swimmer's ear", these infections usually develop after prolonged exposure to water because the ear canal becomes vulnerable when it repeatedly comes into contact with water.
Early symptoms are often mild, but untreated cases risk spreading to other parts of the body. When this happens, the symptoms can be much more serious and severe. Symptoms are discussed separately according to the stage of the disease.
Early symptoms of external ear infections can be listed as;
- External ear canal itching,
- Rashes
- Discomfort in the auricle,
- Odorless discharge from the ear
Mid-term symptoms can occur as;
- Increasing ear pain,
- Intensified ear canal itching,
- Increased redness,
- Excessive discharge of pus,
- Ear congestion
- Decreased hearing
These are more intense symptoms.
Advanced stage symptoms are;
- Swelling in the outer ear,
- Severe pain in the face, neck, and ear area,
- Swollen neck lymph nodes,
- High fever
- Complete obstruction of the ear canal
are the situations in which they occur.
If one or more of the above symptoms are present, a specialist should be consulted urgently. Treatment is much easier and faster in cases diagnosed early.
What Causes External Ear Infections?
The main risk factor for external ear infections is fungal or bacterial infections. The wet and moist structure of the mucosa in the external auditory canal causes it to be easily affected by bacterial infections.
Especially frequent showering, swimming in the sea or pool, and frequent cleaning of earwax increase the risk of infection.
Inserting foreign objects into the ear can also cause damage to the outer ear mucosa. Such actions accelerate the growth of bacteria and fungi in the ear.
How are external ear infections treated?
Most external ear infections can be treated with medication, but it is important to use medication as directed by a doctor. Using the wrong medication can exacerbate the problem and cause serious damage. In cases of dirt or fungus in the ear, the dirt in the ear must first be cleaned. Then a medicine recommended by the ENT specialist can be used.
External ear infections can be diagnosed by physical examination. Usually, swelling, discharge and redness in the ear are sufficient for diagnosis. Since inflammation in the ear differs from person to person, ear drops may be preferred in addition to medication. In cases where the pain is severe, painkillers are recommended.
It is important to continue medication for the period recommended by the physician and to protect the ear from sensitive movements.
Usually, with regular treatment, the severity of the infection decreases within 3 days and disappears completely within 10 days. In external ear infections detected at an early stage, the symptoms are much milder and the treatment process is faster.
 Language
Language
 Turkish
Turkish
Recent Comments